Inflation is a basic financial indicator that measures the expansion in the general price level of goods and services after some time. It is fundamental for states, businesses, and investors to understand inflation patterns as it can essentially affect different parts of an economy, from buyer buying capacity to investment choices. One of the critical strategies for ascertaining inflation rate is by using Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data. In this article, we will investigate how to calculate inflation rate using GDP, with an emphasis on nominal GDP.
What Is GDP And Nominal GDP?

Image Source :- https://rb.gy/m6t32
Prior to digging into how to calculate inflation rate using GDP, it’s significant to understand what GDP and nominal GDP are:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP is an extensive proportion of a country’s financial exhibition. It addresses the total monetary value of all goods and services created inside a country’s lines during a particular time span, commonly a quarter or a year. GDP can be communicated in two essential ways: nominal GDP and genuine GDP.
Nominal GDP
Nominal GDP is the total value of goods and services created inside a nation’s boundaries, estimated in current market prices. It doesn’t account for the inflation, so it addresses the GDP at the ongoing price level.
What Is The Formula To Calculate The Inflation Rate Using GDP?
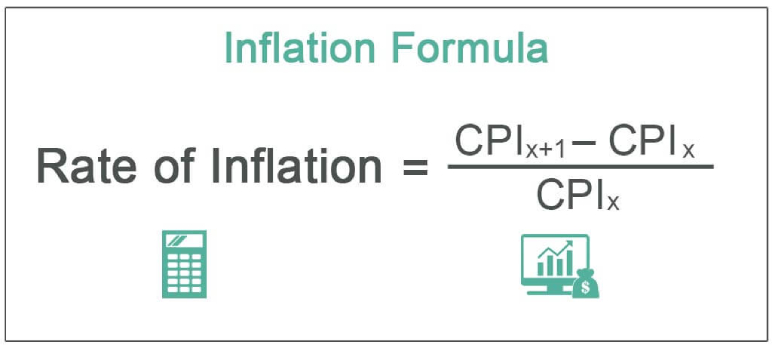
Image Source :- https://tinyurl.com/mtzaazef
To calculate the inflation rate using GDP, you’ll need data for the nominal GDP for at least two time periods, usually two consecutive years. The formula for calculating the inflation rate is as follows:
((GDP deflator in current year – GDP deflator in previous year) / GDP deflator in previous year) x 100
Where:
– Nominal GDP_2: The nominal GDP for the later time period (e.g., the current year).
– Nominal GDP_1: The nominal GDP for the earlier time period (e.g., the previous year).
Step-By-Step Guide For How to Calculate Inflation Rate Using GDP
Presently, how about we separate the most common ways to calculate the inflation rate by using the GDP into basic steps:
Step 1: Gather The Data
Collect the nominal GDP data for the double cross time frames you need to think about. Guarantee that the data is reliable and accurate, ideally from official government sources or trustworthy economic databases.
Step 2: Apply The Formula
Plug the values of Nominal GDP_2 and Nominal GDP_1 into the formula referenced before:
Inflation Rate = ((GDP deflator in current year – GDP deflator in earlier year)/GDP deflator in earlier year) x 100
Step 3: Calculate The Inflation Rate
Perform the computations as demonstrated in the formula. The result will give you the inflation rate as a rate.
Step 4: Interpret The Result
The calculated inflation rate addresses the rate expansion in the general price level of goods and services between the double cross periods. A positive inflation rate shows increasing prices, while a negative inflation rate suggests falling prices (flattening).
Importance Of Calculating Inflation Rate Using GDP

Now you know the basic tricks of how to calculate inflation rate using gdp? Along with that you also have to Understand the calculations of the inflation rate using GDP is pivotal for a few reasons.
Economic Analysis
It allows economists and policymakers to evaluate the strength of an economy. High inflation can dissolve buying power, while low or negative inflation can flag economic stagnation or deflationary pressures.
Monetary Policy
National banks use inflation data to settle on informed conclusions about loan fees and monetary policy. Controlling inflation is often an essential objective of national banks.
Investment Decisions
Investors depend on inflation data to pursue informed investment choices. High inflation can disintegrate the genuine profit from investments, making it important for investors to change their strategies accordingly.
Business Planning
Businesses use inflation data to set prices, go with production choices, and plan for what’s to come. Accurate inflation rate estimations assist them with adjusting to changing economic circumstances.
Government Policy
Governments use inflation data to formulate economic arrangements, including financial measures, to settle the economy and safeguard the standard of living of their residents.
Limitations And Considerations You Have To Maintain While Calculating The GDP?

While calculating inflation rate using GDP is an important tool, it has a few limitations:
| Base Year Effect | Calculating inflation based on nominal GDP depends on a base year for correlation. Changes in the base year can influence the calculated inflation rate. |
| Doesn’t Account For Quality Changes | It doesn’t consider enhancements in that frame of mind of goods and services over the long haul, which can influence the genuine effect of price changes. |
| Excludes Non-Market Activities | GDP may not catch non-market activities, for example, neglected family work and the underground economy. |
| Data Reliability | The exactness of GDP data and inflation rate estimations relies upon the quality and reliability of the basic data sources. |
How To Monitor The Inflation Trends?

Monitoring inflation trends is fundamental for remaining informed about the condition of an economy and making ideal adjustments to monetary strategies. This is the way you can utilize inflation rate data effectively:
Regular Updates
Monitor inflation rate data updates, which are often delivered by government offices on a month to month or quarterly premise. These reports give the most recent information on price changes in the economy.
Benchmark For Investments
Investors can involve inflation rate data to set reasonable return expectations for their investments. By contrasting investment returns with the inflation rate, they can survey whether their investments are lagging behind rising prices.
Cost Of Living Adjustments
Representatives and retired folks can profit from understanding inflation trends. While arranging salary increments or taking into account cost of living adjustments to retirement pay. Haggling for wage builds that essentially match the inflation rate keeps up with buying power.
Business Strategy
Businesses can change their valuing strategies and production plans based on inflation rate data. They can likewise utilize this information to arrange contracts and oversee costs effectively.
Asset Allocation
For portfolio diversification, investors might consider designating assets that historically have shown versatility notwithstanding inflation, like products, and inflation-protected securities.
Inflation Expectations
The inflation rate can impact buyer behavior and inflation expectations. At the point when individuals expect higher future inflation, they might increase spending in the present, possibly affecting general economic action.
Conclusion

Calculating the inflation rate using GDP, explicitly nominal GDP, is an essential tool for evaluating economic wellbeing and pursuing informed monetary choices. This information is priceless for economists, policymakers, businesses, investors, and people the same, as it helps them adjust to and explore economic landscape. Understanding how to calculate inflation rate using GDP is a significant skill that adds to economic education and informed direction.
Have A Look :-
- Steve Harwell, The Former Lead Singer Of Smash Mouth, Has Died At 56
- Brian Kelly Calls Lsu A ‘Total Failure’ After Loss To Florida State. No Argument Here
- Meta Attempting To Capitalize On WhatsApp’s Popularity With New Monetisation Strategies: Report

